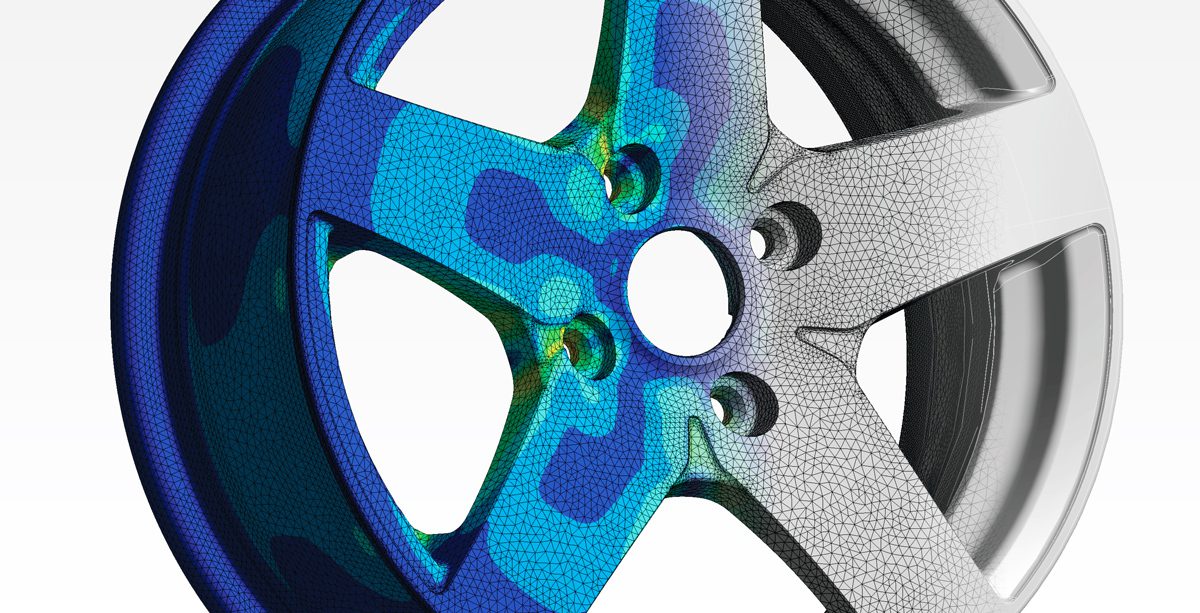
Introduction
Reverse engineering holds a prominent place as a powerful tool for understanding, analysing, and innovating upon existing parts or systems. While the term might sound complex and mysterious, reverse engineering is essentially a process of deconstructing and examining something to reveal its inner workings, design principles, and functionalities. In this blog, we will explore its purpose, methodologies and the role it plays in fuelling innovation.
Defining Reverse Engineering
Reverse engineering is the systematic approach of deciphering the design, functionality, and construction of a product or system through careful analysis and investigation. It involves taking an existing product or system and working backward, often with the aim of understanding its intricacies, replicating its features, or improving upon its design.
Why is Reverse Engineering Performed?
Reverse engineering serves various purposes across different industries and sectors. Below are some common reasons why reverse engineering might be used:
Understanding and Documentation
Engineers can gain an in-depth understanding of how a product or system works. By deconstructing and analysing it, they can document its design, components, and interactions, which can be valuable for future reference.
Replication and Compatibility
This can be useful when spare parts are needed or when compatibility with a particular technology or system is required. By reverse engineering, manufacturers can reproduce products that are no longer available or create compatible components.
Improving Designs
By examining existing products or systems, engineers can identify shortcomings, inefficiencies, or design flaws, which can then be addressed and rectified. This process contributes to enhancing product quality and performance.
Our Reverse Engineering Process:
Our process of reverse engineering normally involves the following steps:
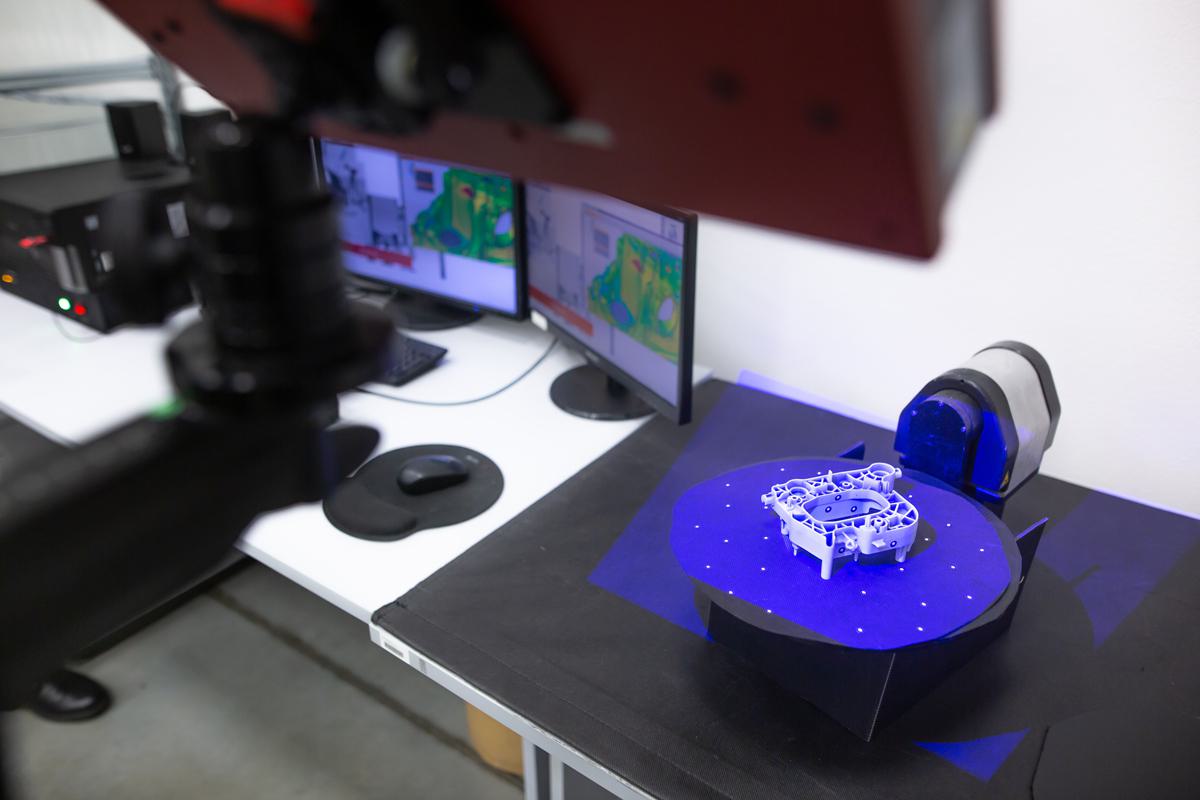
3D Scanning
We offer various types of contact and non-contact 3D scanning services, each varying on the project’s requirements. Typically, we’d use a handheld 3D scanner or arm to obtain a 3D scan of the part.
Importing the data
Once we have collected the 3d scan data, we align it using PolyWorks|Inspector™. This process can vary largely dependent on the object’s features. With the data aligned, reverse engineering can begin using 4 simple steps based on the software solution used:
Create Curve Network
Create magnetised curves onto the polygonal model to delineate the features of the model, such as boundaries and fillets. Add additional curves to complete the curve network.
Generating and Fitting NURBS Patches
Generate NURBS patches from the curve network. Fit the NURBS patches to the underlying polygonal model. The patch flexibility can be adjusted to improve fitting error.
Review Results and Edit Curves and Patches
Review the surfacing results using colour maps. Check the fitting errors, positional & tangential deviations and the curvature map. Where necessary, edit the NURBS patches by customising fitting parameters, adding or editing curves, or using trimmed patches.
NURBS Model from Patches
Once editing is complete, a final fit operation using all NURBS patches for optimal results is recommended. The patches can then be used to generate a NURBS model, which may be exported as IGES or STEP files.
Get in touch
For quality reverse engineering services or to obtain further information, feel free to reach out to our team of skilled experts. We welcome your inquiries and are eager to assist you in any way possible.